Fair Market Value Insights for Multi-Tiered Therapy Service Agreements
Christa Shephard
October 2, 2024
Effective October 8, 2024, Carnahan Group has joined VMG Health. Learn more.
October 15, 2024
Written by Clark Wilson, CVA; Greg Begun; and Ash Midyett, CFA
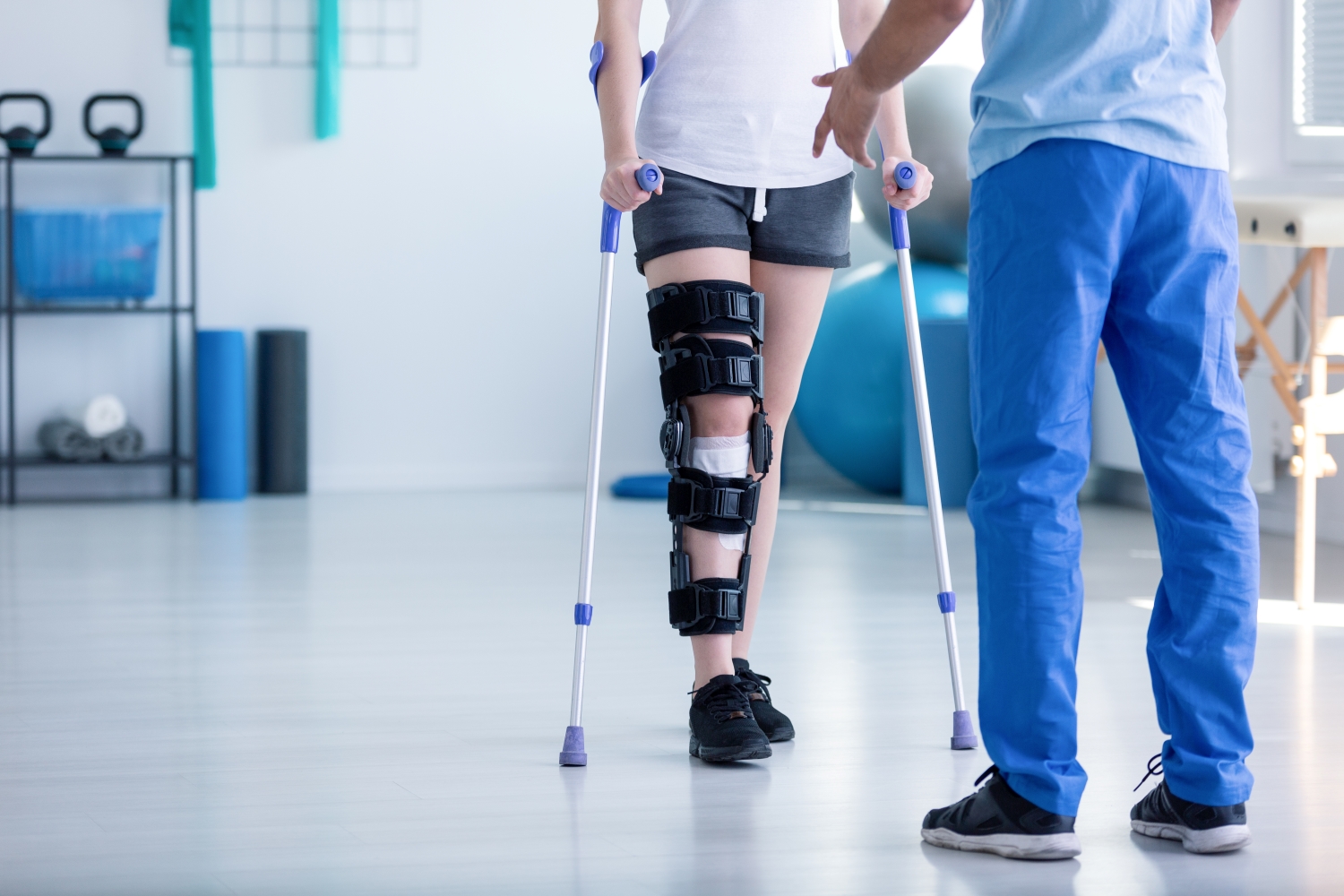
In the broadest sense, remote monitoring refers to a physician assessing a patient’s health through the use of a medical device or software while physically away from the patient. There are two main types of remote monitoring: remote patient monitoring (RPM) and remote therapeutic monitoring (RTM). RPM focuses on gathering physiological data from medical devices attached to the patient’s body, while RTM focuses on non-physiological data that is generally self-reported.
As it relates to physical therapy, RTM can be used to treat and monitor a wide range of conditions, including musculoskeletal conditions, respiratory conditions, geriatric conditions like osteoporosis, and others. Given the broad range of RTM services, there is a growing list of software providers targeting specific and use cases. Some of these entrants include Medsien, Owlytics Healthcare, and Zimmer Biomet, all of which have proprietary RTM software platforms.
The clinical advantages of RTM include improved adherence to treatment plans, enhanced recovery speeds, reduced re-injury rates, and increased patient satisfaction and engagement. Reducing the chance of reinjury and the number of post-injury visits may increase member satisfaction while enhancing data collection to improve treatment and outcomes. Practices may also see increased patient volumes through improved patient access to care and diagnostics, while minimizing the need for unnecessary in-person appointments.
As a new method of patient engagement, research on the efficacy of RTM remains limited. While research often considers remote monitoring as an effective method of treatment for many conditions, limited research specific to RTM exists for physical therapy applications. Additionally, critics often cite data privacy concerns as a primary headwind for further industry adoption.
In response to the growing adoption of RPM and RTM, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) first introduced CPT codes for RPM in 2018 and for RTM in 2021. Since the CPTs were first introduced, CMS has amended billing rules multiple times in response to the pandemic. As of the 2024 Final Rule, CMS allows for billing “incident to” under the direct supervision of a qualified provider (physical therapists, occupational therapists, and speech-language pathologists). RTM and RPM must also be delivered via an approved medical device (which may include software) as certified by the FDA.
The care lifecycle for RTM can generally be characterized by an initial diagnosis, in person or via a telehealth visit, followed by periodic monitoring of the condition, telehealth check ins, or exercise appointments. A provider must monitor a patient for at least 16 days of a 30-day period. As the typical physical therapy course of treatment can range from a few weeks to a couple months, it is easy to understand how RTM may be worked into the treatment life cycle.
RTM is newer than RPM, and payers have been slower to adopt coverage for RTM services as a result. Approved codes are relatively narrow in the scope of conditions covered. Medicaid coverage varies by state, and many states do not have a clear policy around reimbursement. Similarly, commercial payers have been slow to adopt coverage and are generally less likely to cover RTM than RPM.
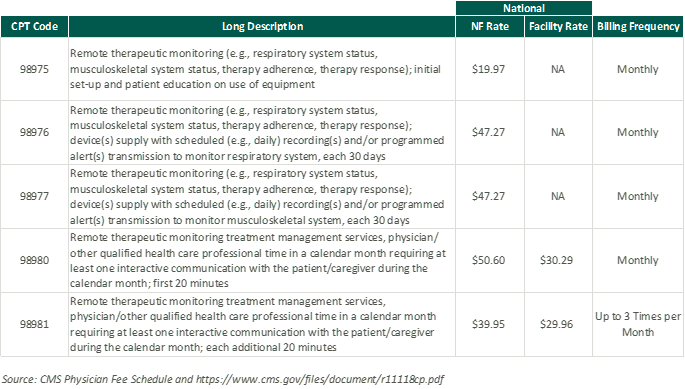
RTM presents a unique opportunity for physical therapy practices to add an additional revenue stream without significant, up-front investment of time or capital and may broaden the practice’s eligible market for care. With the nearly ubiquitous adoption of mobile phones and growing popularization of fitness wearables, the cost of care for physical therapy RPM and RTM is primarily driven by the cost of software to administer the service ($15–$40 per month) and clinician time.
The RTM industry is in the early stage of the industry lifecycle, characterized by fragmentation, high margins, and a robust growth outlook. Current estimates by the Bipartisan Party Center suggest RPM adoption has been limited but is growing quickly, with 594 monthly claims per 100,000 Medicare enrollees as of 2021, which represents a six-fold increase since 2018. It is too early to say whether RTM will follow a similar growth trajectory. Statistics on usage and efficacy remain limited given the novelty of the technology and the fragmentation of its end market. For instance, there are over 37,000 outpatient rehabilitation clinics in the United States with the largest provider only controlling approximately 5% of the market.
In recent years, the adoption of RPM and RTM has been catalyzed by three primary headwinds: technological progress and the proliferation of mobile devices, an industry-wide shift toward value-based care, and the COVID-19 pandemic. For years, insurance payers, regulators, and thought leaders have heralded the adoption of value-based care initiatives to better align the cost of care with improved patient outcomes. RPM and RTM facilitate data collection and may improve patient outcomes while reducing costs through enhanced recovery speed, improved adherence to treatment plans, reduction in re-injury rates, and improved patient satisfaction and engagement. As value-based care continues to gain market share, RTM technology will likely benefit. The confluence of expanded coverage, patient demand, clinical research, and value-based care advocacy will likely bolster RTM adoption among physical therapy providers. While growth projections remain limited, Global Market Estimates predicts annual RTM market growth in the high teens over the coming years. Physical therapy business operators will likely continue to adopt RTM.
Physical therapy and remote patient monitoring. (2022). Telehealth.HHS.gov. https://telehealth.hhs.gov/providers/best-practice-guides/telehealth-for-physical-therapy/physical-therapy-and-remote-patient-monitoring
Saag, JL & Danila, MI. (2022). Remote Management of Osteoporosis. Curr Treatm Opt Rheumatol. DOI: 10.1007/s40674-022-00195-4. Epub 2022 Sep 2. PMID: 36068838; PMCID: PMC9438367.
ROI of RPM CCM and RTM. (n.d.). Humhealth. https://www.humhealth.com/blog/roi-of-rpm-ccm-and-rtm/
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) CPT Code Billing Summary. (n.d.). Healthsnap. https://healthsnap.io/resources/rpm-billing-overview/#:~:text=CPT%20Code%20Billing%20Summary&text=In%202018%2C%20CMS%20began%20providing,reimbursement%20associated%20with%20these%20codes.
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). (2022). CMS Manual System. CMS. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/r11118cp.pdf
CMS.gov. Calendar Year (CY) 2024 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule Final Rule. (2023). CMS. https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/calendar-year-cy-2024-medicare-physician-fee-schedule-final-rule
Thomas, JJ. (2022). How long is physical therapy session? Primal Physical Therapy. https://primalphysicaltherapy.com/how-long-is-physical-therapy-session/
Curtis, J., et. al. (2024). The Future of Remote Patient Monitoring. Bipartisan Policy Center. https://bipartisanpolicy.org/report/future-of-remote-patient-monitoring/
U.S. Physical Therapy (USPh). (2024). USPh IR Presentation Q1 2024. U.S. Physical Therapy. https://www.usph.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/USPH_IR_Presentation_Q1_2024_FINAL.pdf
Global Market Estimates (GME). (2024). Global Remote Therapeutic Monitoring Market Size. Global Market Estimates. https://www.globalmarketestimates.com/market-report/remote-therapeutic-monitoring-market-3954#:~:text=The%20global%20remote%20therapeutic%20monitoring,getting%20infected%20by%20the%20virus
October 10, 2024
Written by Ingrid Aguirre, CFA; Don Barbo, CPA/ABV
A solvency opinion is a professional assessment of a company’s financial health, specifically its ability to meet its long-term obligations. This opinion evaluates whether a company is solvent—meaning its assets exceed its liabilities—based on both current and projected financial conditions and that it has the ability to pay its obligations within a specified amount of time if required by lenders. A solvency opinion serves as a critical tool in corporate finance and transactional contexts, providing stakeholders with confidence in a company’s financial viability.
Solvency opinions are vital for ensuring compliance with various legal and regulatory requirements. They assure boards of directors, shareholders, and lenders that financial decisions—such as mergers, acquisitions, and dividend distributions—are made with a clear understanding of the company’s financial standing.
By obtaining a solvency opinion, companies can mitigate risks associated with potential insolvency claims. A well-supported opinion can protect directors and officers from liability by demonstrating that they acted in good faith and made informed decisions based on sound financial analysis.
A credible solvency opinion enhances transparency and builds trust among investors, creditors, and other stakeholders. It reassures them that the company is on solid financial footing, thereby facilitating smoother transactions and negotiations.
In a litigation context, solvency opinions play a pivotal role.
If a company faces lawsuits related to insolvency, such as fraudulent transfer claims, an independent solvency opinion can serve as a robust defense. It provides evidence that the company was solvent at the time of the transaction in question, helping to protect against accusations of misconduct.
Solvency experts can be called to provide testimony in court, explaining the methodologies and analyses that led to the solvency opinion. Their insights can clarify complex financial matters for judges and juries, lending credibility to the company’s position.
In disputes involving insolvency, a well-prepared solvency opinion can facilitate settlement discussions. It provides a factual basis for negotiations, helping to establish fair terms based on the company’s actual financial situation.
VMG Health provides comprehensive solvency opinions tailored to your specific needs. Our team of financial experts uses rigorous analysis and proven methodologies to ensure our opinions stand up to scrutiny, both in and out of the courtroom.
Our services include:
Secure your company’s financial future and protect your interests with a reliable solvency opinion from VMG Health. Contact us today and discover how we can help you navigate the complexities of financial integrity and legal compliance.
Hayes, A. (2024). What Is Solvency? Definition, How It Works With Solvency Ratios. Investopedia. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/solvency.asp
Jacobsen, C. (2018). Solvency Opinions: Legal Insights and Best Practices for Valuation. BV Research Pro. https://www.bvresources.com/articles/training-event-transcripts/solvency-opinions-legal-insights-best-practices-for-valuation
Jacobson, C. A., & Selbst, S. B. (2014, July 9). BVR’s Advanced Webinar Series on Valuations for Business Transactions: Part 1: Solvency Opinions [Webinar]. Business Valuation Resources LLC.
August 13, 2024
Written by Savanna Ganyard, CFA; Joshua Miner; Chance Sherer, CVA; and William Teague, CFA, CVA
Cano Health, Inc., headquartered in Florida, is a value-based care delivery platform that specializes in primary care for seniors. In February 2024, Cano announced it would enter a reorganization process under Chapter 11 bankruptcy. Less than six months later, on June 28, 2024, the company announced a successful conclusion of its court-supervised restructuring. The company, now private, is looking forward to a brighter future under a more focused strategy.
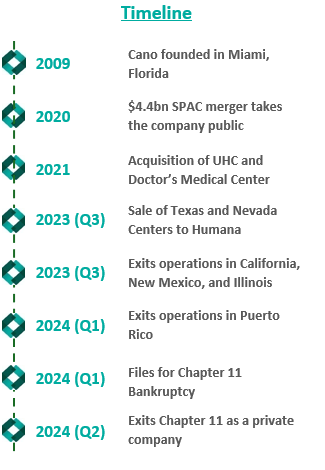
Founded in 2009, Cano began developing its core business as a value-based provider in Florida. The company employs a capitated care model and places a large focus on preventative care and accessibility. The company’s membership is largely comprised of Medicare Advantage, Medicaid, and ACO REACH. As Cano grew, it added complementary service offerings, such as a care management program, a prescription program, and in-home medical visits. These services were meant to prevent hospital admissions and readmissions, increasing Cano’s revenue while decreasing patient total cost of care in the capitated care model.
To further drive growth, the company began to pursue an aggressive policy of expansion through de novo development, acquisitions, and affiliations. The company grew from two markets and 13,700 members in 2017 to 15 markets and 106,000 members by 2020.
In 2021, the company went public in a $4.4 billion merger with a special purpose acquisition company (SPAC) that provided $1 billion in cash proceeds to the company. After going public, Cano continued to fuel growth through acquisitions. In 2021, the company acquired Miami-based University Health Care in a $600 million deal and Doctors Medical Center in a $300 million deal. The company added five states and 121,000 members in 2021, resulting in a total of nine states and 227,000 members. The company continued this growth throughout 2022, ending the year in 10 states and with 310,000 members.
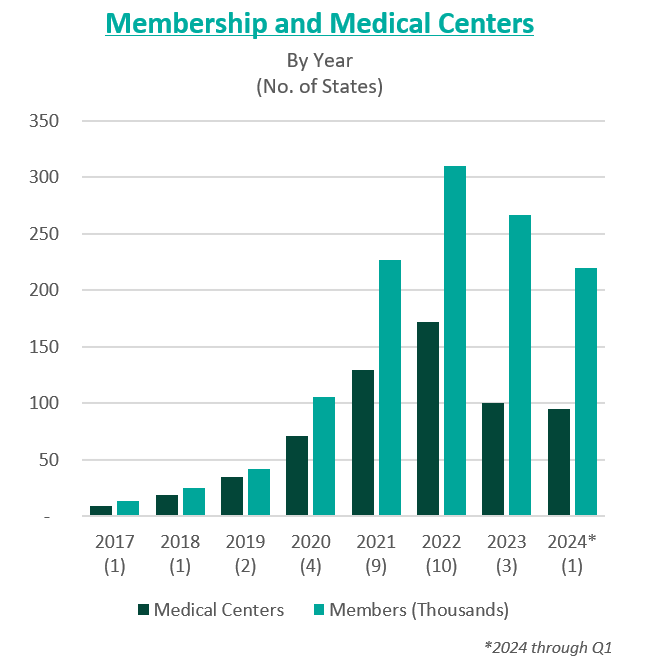
However, in these years of high growth following going public, the anticipated benefits of these acquisitions did not materialize. The company was also affected by industry and regulatory headwinds, including increasing third-party medical costs and a looming Medicare Risk Adjustment Model (V28). On top of these issues, Cano continued to add debt and fell behind on debt repayments. Throughout 2022 and 2023, Cano reported significant losses and an accumulation of $1.2 billion in debt. For context, the company had $1 billion in assets as of December 31, 2023.
In February 2023, Cano entered into a side-car credit agreement with certain lenders. At the end of March 2023, the company’s market capitalization had decreased 90% from its price at the time of its SPAC merger. In April 2023, three board members resigned in protest of company decisions and performance. A couple of months later, the CEO, Marlow Hernandez, stepped down after pressure from shareholders and the former board.
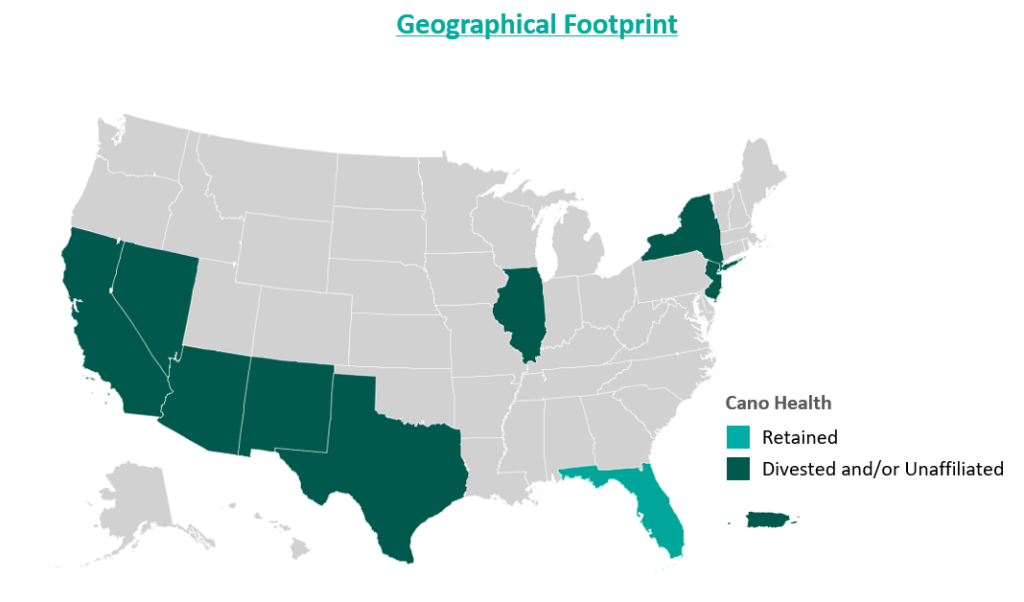
In an attempt improve the company’s performance and cover its liabilities, Cano began to divest its assets. The divestment process began in 2023 prior to the Chapter 11 filing, when the company sold its entire Texas and Nevada portfolio to CenterWell Senior Primary Care, a Humana subsidiary. The net proceeds of the transaction were utilized to pay down debt.
During the second half of 2023, the company also closed medical centers and exited operations in California, New Mexico, and Illinois. These three states represented approximately 5,000 members and 17 medical centers. The company received $19.9 million for the divestiture of certain specialty practices in Florida and assets located in California and Illinois, the net proceeds of which were used as working capital. Cano closed the remaining medical centers in these three states. Finally, Cano successfully exited operations in Puerto Rico at the beginning of 2024.
Despite these transformation efforts, Cano entered into voluntary Chapter 11 proceedings and a Restructuring Support Agreement with most of its lenders in February 2024. The agreement’s primary goal was to reduce debt and position the company for long-term success through cost-cutting measures.
In July 2024, Cano emerged from Chapter 11 as a reorganized private company. The company successfully reduced its debt burden by $1 billion by converting it into equity in the form of common stock and warrants. Additionally, existing investors have contributed an additional $200 million investment to support business operations.
Furthermore, Cano exited its underperforming markets, choosing to focus on its core Florida market. During the bankruptcy process, the court allowed Cano to reject 72 leases in six states. These were sites of offices and medical centers that the company no longer uses.
As established during proceedings, the company’s operational strategy going forward centers around optimizing cost and continuing to evaluate asset performance. To date, Cano is on track to achieve $290 million in cost reductions by the end of 2024. Key drivers of this cost reduction include negotiating with payers, reducing operating costs through decreasing the number of permanent staff, and cutting non-essential spending. In addition, the company is prioritizing Medicare Advantage and ACO Reach lines of business.
Essential to understanding Cano’s emergence from bankruptcy is the amount of divestment the company has undergone. At its peak, Cano operated in nine states and Puerto Rico either directly or through affiliates. To improve operations, the company terminated most of its affiliate partnerships and began to divest many of its operations. Following the reorganization process, the company only operates in Florida. Prior to bankruptcy, Cano had 143 locations in Florida, now reduced to 83 locations.
Cano’s largest asset sale was its centers in Texas and Nevada to CenterWell in a deal worth $66.7 million. At closing, the centers covered 14,450 members and 24 medical centers. These figures imply a multiple of $4,600 per member.

In December 2023, the company commenced a sale process for its ACO Reach line of business. The company has engaged with several bidders, but the transaction has not yet materialized. Cano’s ACO Reach business, which comprises 93,300 members, is projected to achieve $32 million in underwriting margin and $11 million in adjusted EBITDA from August to December 2024. The company also continues to explore sale opportunities related to its Medicaid line of business, which is expected to represent 36,200 members in 2024.
Cano’s financial projections estimate $2.9 billion in revenue and 233,000 members during fiscal year (FY) 2025, growing to $3 billion and 239,000 members by FY 2028. During the same period, the company’s adjusted EBITDA is projected at $125 million, growing to $199 million.
Post-reorganization, the estimated value of Cano at the enterprise level was between $580 million and $720 million. The valuation reflects implied Year 1 (2025) multiples at the midpoint of 5.2x adjusted EBITDA and approximately $2,800 per member.
In June 2024, Cano successfully emerged from bankruptcy as a private company with an improved capital structure and more focused operations. The reduced debt burden, coupled with a $200 million injection of capital, has relieved some pressure on the company as it moves forward. Cano has already made significant progress towards its FY 2024 cost reduction goal, achieving $270 million in cost savings and productivity improvements through the first half of the year. Currently, Cano is focused on its Florida operations but has not ruled out a more prudent expansion in late 2025 or 2026 if it continues to meet its financial goals.
Cano Health, Inc. (n.d.). Press releases, public filings, and investor presentations. Retrieved from www.canohealth.com.
Cano Health. (2023, July 18). Cano Health announces successful emergence from Chapter 11. PR Newswire. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/cano-health-announces-successful-emergence-from-chapter-11-302186063.html
Cano Health. (2023, June 7). Cano Health announces agreement with unsecured creditors committee and court approval of disclosure statement for its reorganization plan. PR Newswire. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/cano-health-announces-agreement-with-unsecured-creditors-committee-and-court-approval-of-disclosure-statement-for-its-reorganization-plan-302152012.html
Cano Health. (2023, March 27). Cano Health enters restructuring support agreement with a significant majority of its lenders to strengthen financial position. PR Newswire. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/cano-health-enters-restructuring-support-agreement-with-a-significant-majority-of-its-lenders-to-strengthen-financial-position-302052889.html
PR Newswire. (2023, March 28). NYSE suspends trading in Cano Health Inc. (CANO) and commences delisting proceedings. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/nyse-suspends-trading-in-cano-health-inc-cano-and-commences-delisting-proceedings-302053778.html
Capital IQ. (n.d.). Investor presentations. Retrieved from Capital IQ website.
Public Information related to Cano Health’s Chapter 11 Plan for Reorganization (Case No. 24–10164). (n.d.). Veritaglobal. Retrieved July 26, 2024, from https://veritaglobal.net/CanoHealth
Klas, M. (2023, July 19). The new Chapter 11 plan for Cano Health aims to exit bankruptcy, cut debt. Miami Herald. https://www.miamiherald.com/news/health-care/article289663459.html
August 7, 2024
Written by Quinn Murray and Ed McGrath, MHA
In the Fall of 2022, we wrote an article discussing not-for-profit health (NFP) system financial performance trends. At the time, NFP systems were experiencing major financial struggles given labor market and supply chain issues coupled with other inflation and industry pressures. While not the primary focus of our 2022 study, VMG Health also raised a concern relative to mid-size hospitals (larger than critical access, but not large enough to provide tertiary/quaternary care). Unfortunately, the concern has proven to be valid as hospital closures and bankruptcies continue. The outlook for these mid-size, independent hospital organizations is not promising given the lack of financial flexibility as larger systems continue the pursuit of acquiring any independent hospitals that have demonstrated any degree of financial success. In 2022, we also noted systems would experience increased competition by private equity–funded niche players and other organizations that could shift profitable services and commercial business from the systems. Their increased presence as disruptors in new markets has accelerated quicker than originally anticipated.
Our 2022 article summarized the financial performance of 21 systems across 32 states, with a combined fiscal year (FY) 2022 operating revenue of $188 billion. As noted in the prior article, the study was not intended to represent a statistically valid sample across all NFP systems, but did include a cross section of systems that provide care to patients in over 30 states with net revenues greater than $2 billion. Of these 21 systems, approximately 15 percent are clients of the VMG Health authors, but the vast majority are not.
Our updated article assesses how those same 21 systems performed in FY 2023 as compared to FY 2022 levels. As a result of this study, our team discovered the importance of understanding the broader implications resulting from the unfavorable financial performance of NFP health systems. This report also discusses the actions our clients and other NFP systems are taking to address the existing financial pressures and to proactively address potential future issues.
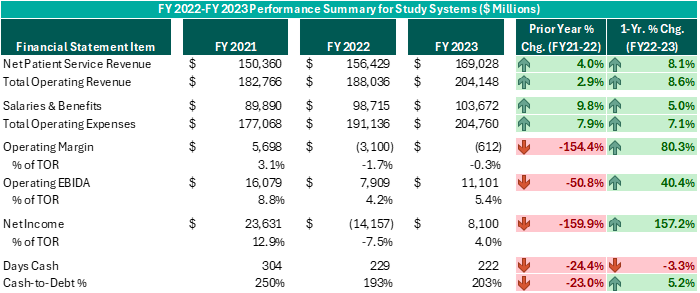
Executive leadership in these systems have made commendable decisions over the past 12–18 months despite ongoing challenges. While operating margins on a combined basis have improved by $2.5 billion from FY 2022 (and combined operating EBIDA improved over $3 billion), these organizations still experienced combined operating losses of ($612 million) in FY 2023. However, while positively trending toward break-even operating margins and 5% or higher operating EBIDA margins is no small feat following the adversity endured nationwide during FY 2022, these levels do not support long-term sustainability. Healthcare systems seeking sustainable financial operations should target operating margins of 3% or higher and operating EBIDA margins of 10% or higher. Those targets may not be achievable for all NFP Health Systems, but consecutive years of operating losses and minimal cash flows are not conducive for strategic growth and reduces an organization’s flexibility to certain strategic investments.
While the performance turnaround noted above is remarkable, the future of NFP healthcare systems continues to be very challenging. Organizations are seeking avenues to develop accretive opportunities to thrive—not just survive. Survival should not be the long-term objective. Systems are exploring and utilizing a variety of options and resources to improve performance, some of which have come to fruition in the past 12–18 months, as evidenced by the financial summary above.
Avenues some of our client system executives have pursued include the following. Note, each market and each situation is unique: One can apply similar approaches, but there is no cookie-cutter or templated solution. Rather, adjust the model to fit the situation as opposed to forcing the situation to fit the model.
To achieve long-term financial success, NFP systems should consider more innovative strategies that complement the evolving healthcare landscape. Patient preferences are not the same as they were 20 years ago, nor is the manner in which healthcare providers deliver care. Competitors and other organizations will capitalize on those who remain complacent and do not adapt. Therefore, sustainable success will require a willingness to adapt to the current industry environment in addition to proactive planning to meet the anticipated future needs of the patients and communities served.
August 6, 2024
Written by Nathan Woods; Frank Fehribach, MAI, MRICS; Kristin Herrmann, MAI, ASA
Healthcare real estate is a critical sector that supports the delivery of medical services, from hospitals and outpatient centers to medical office buildings and nursing facilities. However, this sector is heavily regulated, with specific laws aimed at preventing conflicts of interest and maintaining fair competition. Among the most influential regulations are the Stark Law, antitrust laws, and the federal Anti-Kickback Statute.
The Physician Self-Referral Law, commonly known as the Stark Law, is designed to prevent conflicts of interest in healthcare. It prohibits physicians from referring patients to receive designated health services (DHS) payable by Medicare or Medicaid from entities with which they have a financial relationship, unless an exception applies. DHS includes a wide range of services, such as clinical laboratory services, physical therapy, and radiology. Some exceptions include in-office ancillary services, equipment and office space rental, and bona fide employment relationships. These exceptions must occur within fair market value except certain in-office ancillary services—which simply allow physicians to refer patients for certain ancillary services, such as lab tests or physical therapy—within their own practice.
1. Financial Relationships: The Stark Law targets various financial relationships, including ownership, investment interests, and compensation arrangements. In the context of healthcare real estate, this means that lease agreements, joint ventures, and other financial dealings involving physicians must be carefully structured to avoid prohibited self-referrals. A self-referral in the context of the Stark Law occurs when a physician refers a patient to a medical facility in which they or an immediate family member have a financial interest, such as ownership, investment, or compensation arrangements.
2. Fair Market Value (FMV): All financial arrangements must be at fair market value. Fair market value is the price at which the property would change hands between a willing buyer and a willing seller, neither being under any compulsion to buy or to sell and both having reasonable knowledge of relevant facts. This requirement ensures payments reflect what would be paid in an arm’s-length transaction and are not influenced by the volume or value of referrals.
3. Exceptions and Safe Harbors: Stark Law provides several exceptions that allow for certain financial relationships if specific criteria are met. For example, the rental of office space exception permits arrangements if they are in writing, specify the terms, have a term of at least one year, and meet FMV standards without considering the volume or value of referrals. The bona fide employment relationships exception permits compensation arrangements between physicians and employers if the employment is for identifiable services, the compensation is consistent with fair market value, and not based on the volume or value of referrals. These exceptions are designed to allow necessary and beneficial financial relationships while preventing conflicts of interest.
Stark Law is known for its complexity. Healthcare real estate transactions must undergo careful legal and financial scrutiny to ensure compliance. Violations can result in severe penalties, including fines, exclusion from federal healthcare programs, and the requirement to repay amounts received for services provided in violation of the law.
Case Studies and Precedents
1. Tuomey Healthcare System Case (2015): Tuomey Healthcare System faced one of the largest penalties under Stark Law, amounting to $237 million. The case revolved around improper financial relationships with physicians, where the compensation was linked to the volume of referrals. This case underscores the importance of structuring compensation arrangements to comply strictly with FMV standards and avoiding any link to referral volumes.
2. Scripps Health Case (2021): Scripps Health in San Diego, California settled allegations related to violations of Stark Law. The health system was accused of compensating physicians at rates above fair market value, which were allegedly tied to the volume and value of patient referrals. The settlement amounted to $1.5 million and highlighted the importance of ensuring physician compensation arrangements strictly adhere to fair market value standards and are not linked to referral volumes.
Antitrust laws, including the Sherman Act and the Clayton Act, aim to promote competition and prevent monopolistic practices. These laws are essential in healthcare real estate, ensuring market power is not concentrated in a way that restricts competition or harms consumers.
The Sherman Antitrust Act, enacted in 1890, is the cornerstone of antitrust legislation in the United States. It prohibits certain business activities that federal government regulators deem to be anti-competitive and that restrict interstate commerce and trade. The act broadly prohibits agreements and practices that restrain trade, such as price-fixing, bid-rigging, and market allocation agreements. It also addresses monopolization and monopolization attempts, aiming to promote fair competition, protect consumers from monopolistic practices, and foster economic efficiency.
The Clayton Antitrust Act, passed in 1914, is an amendment to the Sherman Act and further strengthens antitrust laws in the U.S. It focuses on specific practices that the Sherman Act did not clearly address, such as price discrimination and exclusive dealing contracts that may substantially lessen competition. The Clayton Act also prohibits mergers and acquisitions that may substantially lessen competition or tend to create a monopoly. It aims to prevent anti-competitive practices and promote fair competition by addressing various forms of conduct that could harm consumers or competitors in the marketplace.
Implications for Healthcare
1. Market Power and Competition: Healthcare providers acquiring substantial real estate operations must ensure these acquisitions do not unfairly limit competition. For instance, controlling a significant number of facilities in a region could raise anti-trust concerns if it reduces consumer choice or leads to higher prices.
2. Collaborations and Joint Ventures: Partnerships and joint ventures in healthcare real operations can also attract antitrust scrutiny. Such arrangements must be structured to avoid anti-competitive effects, such as price-fixing or market division.
3. Mergers and Acquisitions: Mergers and acquisitions involving healthcare operations are subject to antitrust review. This process involves analyzing market share, potential benefits, and any anti-competitive impacts. Transactions that significantly lessen competition or create monopolies can be challenged and blocked.
Navigating antitrust laws requires a thorough understanding of market dynamics and regulatory requirements. Transactions in the healthcare sector often undergo detailed scrutiny by regulatory bodies like the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). Legal and financial experts must conduct comprehensive market analyses to demonstrate that transactions will not harm competition.
Case Studies and Precedents
1. FTC v. Advocate Health Care Network (2017): The FTC challenged the merger of Advocate Health Care Network and NorthShore University Health System, arguing that it would reduce competition and lead to higher prices for consumers in the Chicago area. The court sided with the FTC, emphasizing the importance of ensuring mergers do not negatively impact market competition.
2. St. Luke’s Health System and Saltzer Medical Group Case (2015): St. Luke’s Health System acquired Saltzer Medical Group, which the FTC argued would reduce competition for adult primary care physician services in Nampa, Idaho. The court ruled against the merger, and St. Luke’s was required to divest Saltzer. This case illustrates the need for careful antitrust review in healthcare mergers and acquisitions.
3. Pennsylvania v. UPMC and Highmark (2014): The state of Pennsylvania filed a lawsuit against UPMC and Highmark, alleging that the two healthcare giants engaged in anti-competitive practices. The case was settled with both parties agreeing to terms that ensured competition in the market, highlighting state authorities’ role in enforcing antitrust laws to protect consumers.
The Anti-Kickback Statute (AKS) is a federal law that prohibits the exchange or offer to exchange of anything of value to induce or reward the referral of business in a federal health care program. This law aims to prevent financial incentives that could corrupt medical decision-making and lead to increased costs for federal healthcare programs.
1. Prohibited Practices: The AKS prohibits any remuneration, including kickbacks, bribes, or rebates, that is intended to induce referrals for services covered by federal healthcare programs. This includes both direct and indirect payments.
2. Safe Harbors: The law provides for certain “safe harbors” that protect specific payment and business practices from prosecution if they meet certain requirements. These include space and equipment rentals, personal services and management contracts, and payments to bona fide employees.
Implications for Healthcare Real Estate
1. Lease Agreements: Lease agreements between healthcare providers and landlords must be carefully structured to ensure they do not involve payments for referrals. For example, rental rates must reflect fair market value and must not be influenced by the volume or value of referrals.
2. Joint Ventures: Joint ventures between healthcare entities and real estate investors must avoid arrangements where returns on investment are linked to the volume of referrals to federally funded healthcare programs.
3. Real Estate Transactions: Real estate transactions must be structured to avoid any implication that payments or benefits are provided in exchange for referrals. This requires detailed scrutiny of the terms and conditions of the transaction.
Ensuring compliance with the AKS requires thorough documentation and a clear separation of any payments from referral activities. Violations of the AKS can lead to severe penalties, including criminal charges, fines, and exclusion from federal healthcare programs.
Case Studies and Precedents
1. United States v. Tenet Healthcare Corporation (2016): Tenet Healthcare settled for $514 million, $368 million for civil penalties, and $145.8 million in criminal penalties to resolve allegations that it paid kickbacks for patient referrals through leasing arrangements. This case underscores the necessity for healthcare real estate transactions to comply with AKS requirements to avoid substantial financial and legal repercussions.8
2. United States v. South Florida Hospital and Healthcare Association (2015): This case involved allegations that a hospital system provided financial incentives to physicians for referrals, which were disguised as above-market rental payments for office space. The settlement highlighted the importance of ensuring that rental payments reflect fair market value and are not tied to referral volumes.
Conducting thorough due diligence and maintaining transparency in financial transactions are essential steps in mitigating risks associated with Stark Law, antitrust laws, and Anti-Kickback Statute compliance. Healthcare business professionals should:
Following established guidelines and best practices can further mitigate compliance risks. Healthcare entities should:
Stark Law, antitrust laws, and the Anti-Kickback Statute play crucial roles in regulating healthcare real estate, ensuring ethical financial relationships and promoting fair competition. While these laws present significant compliance challenges, understanding their provisions and implications is vital for healthcare real estate professionals. By adhering to best practices, conducting thorough due diligence, and seeking expert guidance, stakeholders can navigate these complex legal landscapes effectively, supporting the healthcare real estate sector’s growth and integrity. The case studies and precedents highlight the importance of compliance and the potential consequences of violations, underscoring the need for careful attention to regulatory requirements in healthcare real estate transactions.
HHS Office of Inspector General. (n.d.). Physician self-referral law [42 U.S.C. § 1395nn]. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Retrieved from https://oig.hhs.gov/compliance/physician-education/fraud-abuse-laws/
Social Security Act, 42 U.S.C. § 1395 (b) (2024). Retrieved from https://uscode.house.gov/view.xhtml?req=(title:42%20section:1395%20edition:prelim)
Treasury Regulation § 1.170A-1(c)(2), 26 C.F.R. (2024). https://www.law.cornell.edu/cfr/text/26/1.170A-1
Federal Trade Commission. (2017, March 22). Advocate Health Care Network. Retrieved from https://www.ftc.gov/legal-library/browse/cases-proceedings/1410231-advocate-health-care-network
Federal Trade Commission. (2015, February 10). St. Luke’s Health System, LTD, and Saltzer Medical Group, P.A. Retrieved from https://www.ftc.gov/legal-library/browse/cases-proceedings/121-0069-st-lukes-health-system-ltd-saltzer-medical-group-pa
Commonwealth v. UPMC. (2015, November 11). Casetext. https://casetext.com/case/commonwealth-v-upmc
HHS Office of Inspector General. (n.d.). Anti-Kickback Statute [42 U.S.C. § 1320a-7b(b)]. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Retrieved from https://oig.hhs.gov/compliance/physician-education/fraud-abuse-laws/
U.S. Department of Justice. (2016, October 3). Hospital chain will pay over $513 million for defrauding United States and making illegal payments. Retrieved from https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/hospital-chain-will-pay-over-513-million-defrauding-united-states-and-making-illegal-payments
August 1, 2024
Written by Sydney Richards, CVA; Erica Veri
The value a brand brings to a strategic partnership is overlooked in many healthcare joint ventures and affiliations. However, healthcare brands may have a significant impact on a partnership’s success. Healthcare brands can suggest top outcomes to communities in the face of intense competition, attract and retain leading providers, and evoke a sense of loyalty and trust among the patient base. In many joint ventures and partnerships, completing a brand valuation allows the licensor to receive a financial return for their contribution of this important asset. Below, we outlined important factors that may be considered in a brand valuation.
Healthcare brands are commonly contributed to a partnership through a license agreement. The structure and terms of the brand licensure can significantly influence the value. For example, a brand license agreement may stipulate payment terms, which can be structured as an upfront equity in a partnership, a fixed annual payment, or a variable (royalty rate) payment. These terms can have a significant impact on how financial risk is or is not shared between the parties, especially for partnerships such as de novo joint ventures. The license agreement can also specify the duration of the brand contribution and specify whether the rights to the brand are exclusive to the proposed licensee or whether the licensor may enter other brand contributions simultaneously.
From the licensor’s perspective, extending the use of their brand to a partner can offer an opportunity to access a larger patient population without sizable investment in capital and infrastructure. A licensor also gains the opportunity to monetize the positive reputation associated with its brand, which has often been built over significant time, investment in expertise and care quality, and marketing spend. While these historical costs may be difficult to quantify, the quality and strength of the brand, especially as compared to peers, can and should be considered in a brand valuation.
One of the ways the brand strength, recognition, and positioning can be considered in the appraisal is through a “with and without” analysis, which seeks to quantify how forecasted earnings would differ for an opportunity with vs. without using the brand. These earnings can be impacted by items such as speed to ramp up for partnered de novo ventures, increased occupancy or utilization due to the community’s association of the brand with high quality care, margin effects of greater economies of scale, or even a favorable payer mix shift.
Additionally, other benefits may be captured in the with and without analysis, including access to clinical integration, clinical trials and research, facilities and equipment planning, and recruiting. If the licensee is a smaller entity with less market share than the licensor, it may desire to leverage the branding entity’s experience and knowledge of best practices while conveying the expertise and reliability of the larger brand to the patient population.
The cost to replicate considers what it may cost to develop and maintain a comparable brand. While many retail brands communicate price and prestige, healthcare brands typically emphasize a company’s quality patient service, positive outcomes, and reliability. A healthcare brand can also attract physicians and help in retaining talent. These qualities may take years, even decades, to develop. While there are certain quantifiable measures that can be included in a brand appraisal, such as advertising and marketing spend to build and maintain a brand, it can be difficult to measure the true costs to replicate brand value for many healthcare brands. Additionally, unless the licensee can generate a return on these costs, it would not be reasonable to assume they would be willing to pay for all historical costs unrelated to a particular licensing arrangement. As a result, this approach is commonly considered but may not directly drive a value indication for the specific payment a licensee should make for the use of the brand.
A licensee’s financial performance may have a material impact on the amount it can expect to pay in a licensing arrangement. Factors such as business stage (start up, growth, or mature), subindustry, margin, and operational capacity or constraints can directly impact the ability of a brand to drive incremental earnings to the licensee through use of the brand. A brand valuation for a license payment between two entities commonly includes a thorough examination of the licensee’s position in the local and greater market, performance compared to peers, and outlook.
There are numerous market sources for brand valuation comparables. While commonly considered and thoroughly analyzed, due to the uniqueness of each licensing opportunity, many lack direct comparability to the royalty rates published in publicly available databases, such as MARKABLES, ktMINE, and Scope Research. To the extent that there are brand comparables, a brand valuation should consider reasonable market ranges for similar assets and transactions.
Compared to many healthcare business or other asset valuations, healthcare brand valuations can be difficult. There can be uncertainty (and differences of opinion) on the go-forward impact a brand may have on a business. Although there are established general market ranges within healthcare segments, there are less direct market comparables compared to other partnership contributions, such as business equity or real estate value, for brands. With VMG Health on your team, you can expect the quality, responsiveness, and expertise your brand deserves to overcome these hurdles and drive a successful brand contribution and lasting partnership.
July 31, 2024
Written by Jordan Nelson
The following article was published by Retina Today.
In recent years, the field of ophthalmology, including the subspecialty of retina care, has witnessed significant transformations driven by private equity (PE) investments. This trend has led to a multitude of changes, both positive and challenging, in how retina practices are structured, managed, and perceived. As these investments continue to shape the landscape, it becomes crucial to examine their effect on patient care. Doing so will help health care providers navigate these practice management changes to ensure that patients continue to receive the highest quality care.
PE firms have become increasingly interested in investing in medical practices, including those specializing in retina care. These PE investments are typically structured through the creation of a Management Services Organization (MSO) that acquires the assets of medical practices while keeping practice entities in place for regulatory purposes.
MSOs provide a range of services to medical practices, such as human resources (HR), revenue cycle management, finance, and accounting. The MSO also provides capital for expansion, while implementing operational changes to improve profitability. Typically, physician owners who sell their practice assets to an MSO reinvest a portion of their sale proceeds into the MSO entity, thus becoming co-investors and part owners alongside the PE firm.
By far, the largest retina MSO is Retina Consultants of America (RCA). RCA received PE funding from Webster Equity Partners in 2020. Today, RCA holds 23 acquired brands, 200 locations across the United States, and hundreds of retina specialists.1 Prism Vision Group, another PE-backed MSO, was initially known as New Jersey Retina prior to being funded by Quad-C Management in 2018. This MSO has made 21 acquisitions, primarily retina practices, but also general ophthalmology practices and ambulatory surgery centers in the Northeastern United States.
Nearly 40 PE-backed eye care MSOs operate in the United States, and nearly all partner with and employ retina specialists, many of whom are part of general ophthalmology groups. Hundreds of millions have been invested in these platforms, which has created a significant shift in how retina practices are managed and operate, with implications for both physicians and patients.
At a Glance
While PE investments can bring financial benefits and operational efficiencies, they also pose several challenges for medical practices. PE ownership often has an investment horizon of 5 to 7 years to produce a +25% return for investors. New management is often hired, bringing with it business management tools that smaller practices may not be used to using, such as annual budgets and board approval for strategic initiatives. PE also requires uniform information systems, leading to significant changes to accounting, practice management, and health record systems.
The C-suite executives of an MSO are incentivized by profitability and enterprise growth. If not careful, an MSO may begin to prioritize process, systems, and profitability over patient experience and outcomes. Administrative burdens and standardized protocols may not align with the personalized approach often associated with medical specialties such as retina care. Downward financial and administrative pressure on physicians can also lead to a lack of clinical excellence.
Despite these challenges, there are strategies physicians and practices can employ to ensure that patients continue to receive excellent care under corporate ownership.
It is not feasible for every physician in a practice that employs dozens (or even hundreds) to have clinical control over the organization; as an alternative, MSOs can establish a Medical Executive Committee (MEC). This is a committee comprised strictly of physicians and has direct access to the MSO’s Board of Directors.
The committee is tasked with representing the general mind of the physicians and ensuring clinical considerations remain a top priority. The MEC works with management to establish annual budgets for new equipment or other technology investments. The MEC is charged with establishing clinical best practices and protocols, monitoring quality metrics, and addressing HR situations that affect clinical care. The goal is to ensure physicians have independent representation at the highest levels of the organization and the clinical autonomy of providers remains sacrosanct.
In some MSOs, the Board of Directors has physician representation, which is good, but not a substitute for an MEC. Within general ophthalmology practices, specialties like retina should be appropriately represented. Geographic representation should also be given consideration, and as MSOs grow, geographic sub-MECs could be useful.
Physicians’ interaction with each other can create a culture of collaboration and accountability. Collaboration often leads to innovative solutions to the challenges physicians face as part of a PE partnership model. Establishing a regular cadence for collaboration can facilitate the open exchange of ideas among care providers. Monthly or quarterly conferences/video calls allows providers to share ideas around clinical quality, new technology or techniques, hiring and staffing best practices, and a general forum to discuss treatment plans for uncommon or difficult patient situations.
In-person collaboration and meetings can also be a positive addition to the practice. While far more expensive than a conference call, face-to-face meetings offer a more personal and concentrated format for physicians to engage with each other.
Corporate-owned practices should support physicians’ continuing education to ensure they stay abreast of the latest advancements in retina care. This can help maintain high standards of care and physician clinical autonomy. At a minimum, practices should include a budget for providers to attend conferences and other education events.
In addition, company management can coordinate with the MEC to create internal education opportunities and training. This might include inviting internal experts to share their knowledge with the broader group or inviting outside industry participants such as academia, health systems, or technology companies to collaborate.
The initial success of most independent practices is dedication to creating a great patient experience. This standard, regardless of ownership, should always be the primary focus. Not only is this the right thing to do for patients, but also for the business.
Building and maintaining a patient-first culture is done by setting the example at the top of the organization. Board of Director and shareholder meetings should allocate as much time to patient-related matters as they do to financial and strategic items. For example, in a one-hour Board of Directors meeting, it is not unreasonable to expect 20 minutes of the agenda to focus on items such as quality metrics, patient satisfaction surveys, and clinical innovation. Much of this can be addressed by the MEC in board meetings.
Corporate-owned practices should establish quality metrics that prioritize patient outcomes and satisfaction. This will likely require investment in staff and technology to collect and analyze data. If knowledge is power, data can be the key to understanding how a practice is succeeding or failing and where it is happening across the platform. Regular monitoring and assessment of these metrics can help identify areas for improvement and ensure high-quality care.
Open and transparent communication between physicians and their local practice administrators is crucial. Just as physicians need dedicated access to the Board of Directors, local practice operators need direct access to the physicians in the practices they are charged with operating. Local practice administrators are on the front line when identifying problems and effectively rolling out new programs. Without effective and open communication, much can get lost between the siloed roles in which administrators often operate.
In the Literature
A recent study published in Ophthalmology found that, after retina practices are acquired by PE, their Medicare spending increases. The researchers looked at a total of 82 practices acquired by PE during the study period (2015-2019) and matched control practices. In the PE-acquired practices, they found a 22% increase, per practice-quarter, in the use of higher-priced anti-VEGF agents (i.e., aflibercept [Eylea, Regeneron]), compared with control, non-PE, practices. This increased usage, averaging an extra 6.5 injections, led to an increase in overall Medicare spending of $13,028 per practice quarter, or 21%.
Practices should empower patients to advocate for their own care. This includes educating patients about their condition, treatment options, and how to navigate the health care system to ensure they receive the best possible care. Patients should have the ability to provide feedback about their experience. Technology can play an important role in patient advocacy, but dedicated staff tasked with patient advocacy is often the best approach to ensure patients have what they need to feel their experience is the priority of the practice.
PE investment in retina practices is here to stay, and it represents a significant shift in the health care landscape. While these investments bring opportunities for growth and efficiency, they also pose challenges for patient care. By prioritizing patient welfare, preserving physician autonomy, and maintaining high standards of care, practices can navigate these changes and ensure that patients continue to receive great care under corporate ownership.
BSM Consulting. Internal Report. 2024.
Prism Vision Group. Accessed April 22, 2024. prismvisiongroup.com
Retina Consultants of America. Accessed April 22, 2024. www.retinaconsultantsofamerica.com
Singh Y, Aderman CM, Song Z, Polsky D, Zhu JM. Increases in Medicare spending and use after private equity acquisition of retina practices. Ophthalmology. 2024;131(2):150-158.
July 23, 2024
Written by Matthew Marconcini, CPA
Selling your company can be an exciting time, filled with potential opportunities for growth and new horizons. Whether your company is accrual based, following GAAP, or it reports on a cash basis, proper preparation for the sale of your company is extremely important. This journey often involves a complex web of financial transactions and negotiations, with numerous parties at the table. Among the critical elements in this process are financial due diligence and performing a quality of earnings (QOE) analysis. The QOE process is a critical aspect of financial reporting and analysis that helps stakeholders, like investors and creditors, assess the reliability and sustainability of a company’s reported earnings.
The QOE analysis can play a pivotal role in shaping the outcome of the sale and can significantly impact the perceived value of your business. Therefore, as management, it is essential to be well-prepared and proactive in assessing and evaluating the quality of your business’ earnings, as it influences the selling price and builds trust and confidence among potential investors and other stakeholders. We have outlined eight steps management can take to best prepare for the QOE process.
Management should have a clear understanding of what QOE means. It assesses the underlying economic substance of reported earnings, ensuring they are not distorted by accounting manipulations or one-time events.
Accurate financial record-keeping is fundamental to high-quality earnings. Management must ensure that financial statements are free from material misstatements and that all transactions are properly recorded.
Transparency is crucial. Ensure all material transactions, both positive and negative, are adequately disclosed in the financial statements and related footnotes.
Maintain consistency in financial reporting practices. Frequent changes in accounting policies can raise questions about the QOE. If policies do change, explain the rationale behind it and the financial impact of the change.
Recognize revenue in accordance with accounting standards only when it’s earned and realizable. Avoid prematurely recognizing revenue or engaging in overly aggressive practices. If your company reports on a cash basis, pulling together the proper data that will show revenue based on date of service rather than the collection date will be key.
Clearly distinguish between one-time or non-recurring events and ongoing operations in financial reporting. Disclose the nature and impact of such events to prevent misinterpretation.
Be prepared to provide a comprehensive and honest analysis of the company’s financial results. Explain the drivers of earnings, changes in accounting policies, and potential future risks and uncertainties. The more support you can provide related to both historical performance and future growth initiatives, the more accurate and comprehensive your analysis.
Take the time to review the various systems used to operate the business and start pulling data together. If certain systems are maintained by third parties, informing them of the situation and discussing what they need to do will create a smoother process. If certain reports don’t have the necessary inputs or data, be prepared to discuss that and what alternative information would be useful.
By considering these guidelines and implementing the underlying thought processes, management can best prepare for the QOE process, demonstrating a commitment to transparency, accuracy, and integrity in financial reporting. This, in turn, builds trust and credibility with investors and other stakeholders, creating a smooth transaction process for management.
June 27, 2024
Written by Joel Gomez, ASA
Before you begin the process of selling your medical practice, it is always in your best interest to ensure your practice’s value is accurately represented. Most buyers of medical practices, including healthcare systems and hospitals, begin the transaction process with a fair market value analysis of the business revenues to determine the purchase price. Unfortunately, many practices in the position of selling are in a break-even or negative cash–flow scenario. In these instances, the value of the practice may be most accurately represented by the fair market value of personal property and real property.
Some buyers opt to have personal property valued on a “desktop” scope of work, relying on data in the form of a depreciation schedule or practice inventory as the basis of the fair market value analysis. While acceptable for fair market value purposes, this approach may not capture all owned personal property.
The first approach for identifying personal property through accounting documents is the use of a depreciation schedule or fixed asset listing (FAL). While real property is easily identifiable (the space is either owned or rented), personal property listings are often less maintained, reliant on an accountant’s tracking of capitalized assets, and may not fully reflect what is owned. When preparing a valuation, an appraiser is always subject to the quality of available data. FALs maintained by an accountant only display equipment that meets the predetermined capitalization cost threshold determined by that accountant. Additionally, some capitalized assets are removed from the FAL once it has fully depreciated according to accounting standards. Providing an equipment appraiser, a FAL as the basis of their appraisal could mean valuable practice assets are not captured.
An on-site inspection and asset inventory by an appraiser allows them to capture all assets on a room-by-room basis, regardless of original purchase cost or visibility on the FAL.
Another alternative to an appraiser performing an on-site inspection is to have a practice employee create the inventory. While this may sound like a good approach initially, information captured by someone other than an appraisal expert tends to be inconsistent. Items captured in one room are missed in the next, and inconsistent asset descriptions will lead to follow-up information requests, requiring the selling practice to invest more work hours.
Hiring an appraisal expert to complete an on-site inventory and inspection of the practice’s tangible personal property ensures personal property listings are maintained, fully reflect what is owned, and include consistent asset descriptions from room to room. VMG Health reviewed a sampling of projects over the past 18 months, across several practice specialties, and noted that when completing a site visit as part of our valuation process, the fair market value conclusion of exam rooms was roughly 60%–70% higher on a per-room basis compared to relying on practice data/inventories.
VMG Health’s qualified equipment appraisers have the knowledge and experience to complete a discrete and comprehensive inventory, gathering all necessary data during the visit and minimizing interruptions to the practice operations and patient flow.
VMG Health’s team of equipment appraisers has over 55 years of experience in the equipment appraisal field across all sectors of the healthcare industry and includes three accredited senior appraisers with the American Society of Appraisers. Since 1995, VMG Health has earned the trust of our clients with extensive expertise in navigating the dynamic factors that influence value. If you are in the process of valuing your practice, use VMG Health’s equipment appraisers to complete an on-site inspection, inventory, and valuation of your personal property.
June 18, 2024
Written by Glenn Morley, Maureen Waddle, and Katrina Whitehair
The aesthetics industry has grown significantly over the past few years, driven mainly by investor-backed consolidation of practices. Whether large or small, buy- or sell-focused, organizations focused on growth should explore acquisition and de novo development strategies. Aligning the right and best growth strategy with your organizational vision is critical and requires an examination of the strategic advantages both options can offer.
Aesthetics practice consolidation typically refers to the trend of medical aesthetics practices and medical spas merging or being acquired by investor-backed organizations. Consolidation in medical aesthetics has gained momentum over the past five years for several reasons:
The de novo strategy is the process of opening a new practice or medical spa or expanding to a new location from scratch. When choosing the de novo path, it is crucial to understand your business model. You need to identify the target market that offers the most significant probability of success in your area. Key population factors to consider include age and financial bands, and the competitive landscape. Consider launching a target market analysis to focus on your ideal region and region and entail customers. You can also evaluate the demographic data in your practice management system, complete focus group research, or hire experts to ensure there will be demand when you build.
A de novo growth strategy can offer compelling advantages, including control over branding, culture development, service offerings, and management. This also allows you to initiate your build with the retail mantra: location, location, location. A de novo strategy may also require a lower initial investment than an acquisition. However, this strategy can be challenging and time-consuming due to factors such as building a patient base, recruiting providers, and a team willing and able to build from scratch. A less arduous approach to de novo location growth is securing an anchor practice poised for expansion, a target geographic location, or an organization with expertise building de novo in other sectors.
An acquisition growth strategy involves purchasing established medical aesthetics practices and integrating them into an existing organization. While this approach offers immediate access to an established patient base and can provide a steady revenue stream, it comes with its challenges and risks. When a business is acquired, careful due diligence is required to ensure the revenue streams, operations, and systems are reliable and scalable. It will also require integrating many components, starting with culture, HR/personnel, marketing, and operational and financial systems.
Owners looking to expand to multiple locations should carefully evaluate the pros and cons of both de novo and acquisition strategies. Furthermore, it is critical to align these strategies with long-term goals, your current organization’s ability to scale, risk tolerance, and existing market opportunities.
Many growth-minded medical aesthetics organizations seek expert guidance in this process. Engaging industry professionals, including financial advisors like VMG Health and BSM Consulting, can offer invaluable insights and steer you toward informed decisions that align with your strategic expansion goals. Once you have a plan, creating a model of your new acquisition or de novo location is essential for a thoughtful approach to growth.
Whether you build a practice from the ground up or acquire an existing one, you must complete thorough due diligence, including examining financial health through day-to-day operations. Early phase due diligence will reward you with greater prosperity and less disruption.
Acquisition or de novo growth strategies offer excellent business owner opportunities; the choice should align with your practice’s risk tolerance and growth goals. Regardless of your chosen strategic growth plan, stay abreast of the changing landscape and dynamics in the expanding medical aesthetics marketplace.
Authors
Related Content